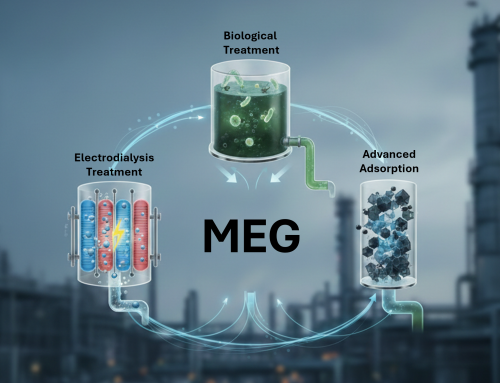
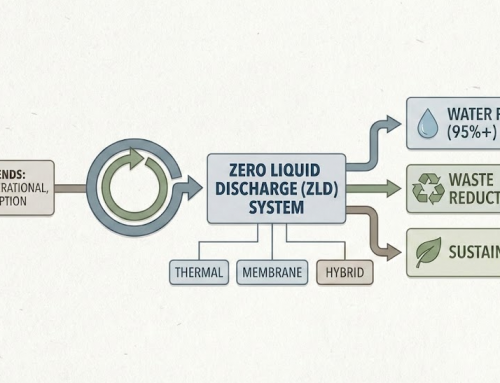
Industrial facilities that operate desalination, membrane separation, and water reuse systems often generate highly concentrated brine streams. These streams contain large amounts of dissolved salts and are difficult to discharge due to environmental regulations. Near-Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) technologies are therefore increasingly adopted to minimize liquid waste, recover valuable resources, and reduce environmental impact.
This study presents an advanced ZLD process based on Electrodialysis Metathesis (EDM) for the treatment of high-salinity industrial wastewater. The proposed approach focuses on efficient salt separation, water recovery, and prevention of scaling during operation.
1. High-Salinity Wastewater Challenge
1.1 Sources of Industrial Brines
Industrial brines typically originate from specific processes, including:
- Reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) reject streams
- Industrial desalination processes
- Water reuse and recycling systems
1.2 Ionic Composition and Discharge Difficulties
These wastewaters contain high concentrations of sodium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, and sulfate ions. Such a high mineral load makes direct discharge or conventional treatment difficult and costly for industrial operators.
2. Electrodialysis Metathesis (EDM) as a ZLD Solution
2.1 Principles of the EDM Process
Electrodialysis Metathesis (EDM) is an electrically driven membrane process that enables selective ion exchange and separation. Unlike conventional electrodialysis, EDM rearranges ionic species to convert scaling-prone salts into more manageable forms.
2.2 Key Operational Features
Key features of EDM identified in this study include:
- Efficient separation of monovalent and divalent ions.
- Conversion of problematic salts into recoverable products.
- Stable operation under high salinity conditions.
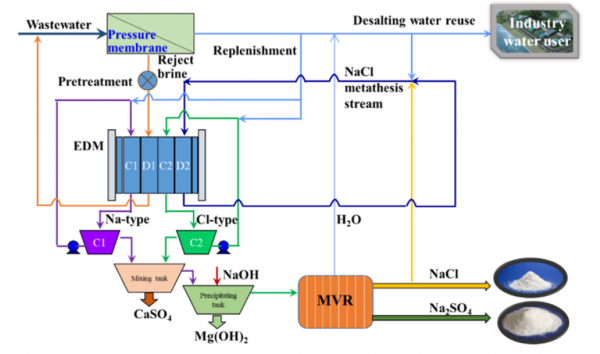
3. Near-Zero Liquid Discharge Performance
3.1 Waste Volume Reduction
The integrated process based on EDM achieved a significant reduction in liquid waste volume. By minimizing the final liquid effluent, the process brings the system very close to zero liquid discharge, meeting strict environmental and regulatory requirements.
3.2 Water Recovery and By-product Generation
The system enables the recovery of reusable water streams and the production of solid or concentrated salt byproducts instead of discharging liquids.
4. Scaling Control and Operational Stability
4.1 Management of Calcium and Magnesium
One of the major challenges in high-salinity wastewater treatment is scaling caused by calcium and magnesium salts. The study demonstrates that EDM effectively controls scaling formation and prevents membrane fouling and operational instability.
4.2 Industrial Reliability
This control is critical for industrial applications where downtime and maintenance costs must be minimized, enabling long-term and reliable operation.
5. Industrial Relevance and Applications
5.1 Suitable Facilities
From a practical and industrial perspective, the proposed ZLD process is suitable for desalination plants, industrial water reuse facilities, chemical and process industries, and facilities facing strict discharge limitations.
5.2 Strategic Goals
The technology supports:
- Water recovery and reuse.
- Salt recovery and resource valorization.
- Reduction of environmental footprint.
6. Advantage and Disadvantage of EDM-Based ZLD Systems
Advantages include high efficiency in treating hypersaline wastewater, lower chemical consumption compared to thermal processes, reduced scaling risk, modular and flexible system design, and compatibility with existing membrane processes.
Disadvantages (as contextually implied by the complexity of the process) involve the need for precise electrical control and the management of specific ionic rearrangements which may require sophisticated engineering compared to standard RO.
7. Conclusion
This study demonstrates that electrodialysis metathesis is a robust and efficient technology for the treatment of high-salinity industrial wastewater with near-zero liquid discharge. By combining salt separation, water recovery, and scaling control, ZLD systems based on EDM offer a sustainable solution for industries seeking to minimize wastewater discharge and maximize resource recovery.
The sources of the images and articles used to write this text are available in this downloadable file: Click here!